Research Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights
Research Highlights 미리보기

Atomic lift-off of epitaxial membranes for cooling-free infrared detection
Prof. Celesta S. Chang
Professor Celesta S. Chang's research team from the Department of Physics and Astronomy has developed an 'Atomic Lift-Off' technique that enables the production of ultrathin, freestanding perovskite oxide membranes—paving the way for high-performance, cooling-free infrared sensors.
Research Highlights Board

Ionic spiderwebs enable cleaning contamination on itself, sensing approaching targets, capturing and releasing those targets
Prof. Ho-young Kim, Prof. Jeong Yun Sun
Spiders use adhesive, stretchable, and translucent webs to capture their prey. However, sustaining the capturing capability of these webs can be challenging because the webs inevitably invite contamination, thus reducing its adhesion force. To overcome these challenges, spiders have developed strategies of using webs t...
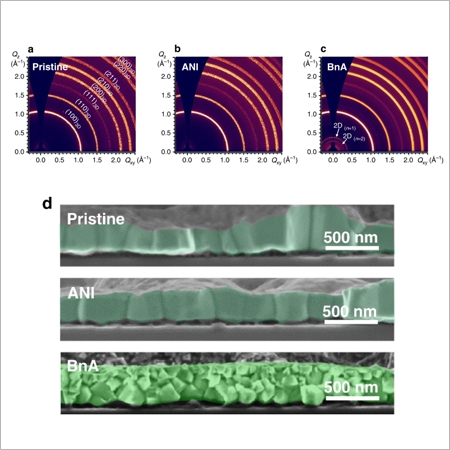
Proton-transfer-induced 3D/2D hybrid perovskites suppress ion migration and reduce luminance overshoot
Prof. Tae-Woo Lee, Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) based on three-dimensional (3D) polycrystalline perovskites suffer from ion migration, which causes overshoot of luminance over time during operation and reduces its operational lifetime. Here, we demonstrate 3D/2D hybrid PeLEDs with extremely reduced luminance overshoot and 21...
Epitaxially Strained CeO2/Mn3O4 Nanocrystals as an Enhanced Antioxidant for Radioprotection
Prof. Taeghwan Hyeon, Prof. Kyungpyo Park
Nanomaterials with antioxidant properties are promising for treating reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related diseases. However, maintaining efficacy at low doses to minimize toxicity is a critical for clinical applications.
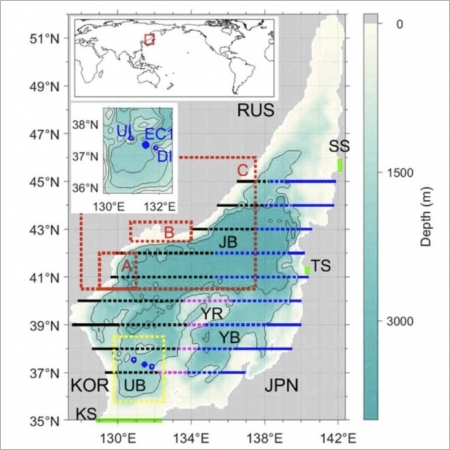
Decadal Changes in Meridional Overturning Circulation in the East Sea (Sea of Japan)
Prof. SUNGHYUN NAM
Meridional overturning circulation (MOC) is vital to distributing heat, freshwater, and dissolved matter in semienclosed deep marginal seas such as the East Sea (ES) (Sea of Japan). As our understanding of the ES MOC remains incomplete, we attempted to fill this research gap. We analyzed the ES MOC and its decadal chan...
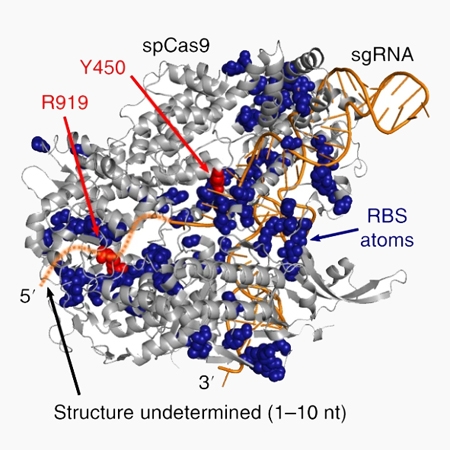
Chemical RNA digestion enables robust RNA-binding site mapping at single amino acid resolution
School of Biological Sciences V. Narry Kim, Jong-Seo Kim
Abstract RNA-binding sites (RBSs) can be identified by liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry analyses of the protein–RNA conjugates created by crosslinking, but RBS mapping remains highly challenging due to the complexity of the formed RNA adducts. Here, we introduce RBS-ID, a method that uses hydrofluorid...
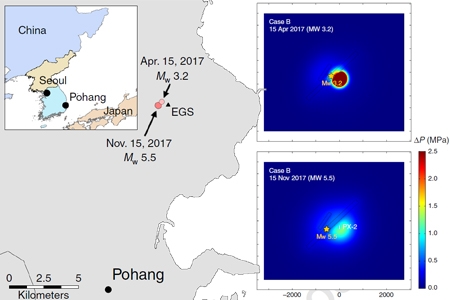
Causal mechanism of injection-induced earthquakes through the Mw 5.5 Pohang earthquake case study
Prof. Lee, KangKun, School of Earth and Environmental Sciences
Causal mechanisms for fluid injection-induced earthquakes remain a challenge to identify. Past studies largely established spatiotemporal correlations. Here, we propose a multi-process causal mechanism for injection-induced earthquakes through a case study of the 2017 Mw 5.5 induced earthquake near Pohang Enhanced Geot...
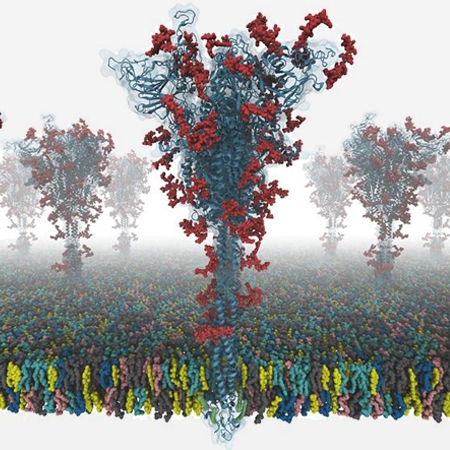
Modeling and Simulation of a Fully-glycosylated Full-length SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein in a Viral Membrane
Prof. Chaok Seok
This technical study describes all-atom modeling and simulation of a fully-glycosylated fulllength SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein in a viral membrane. First, starting from PDB:6VSB and 6VXX, full-length S protein structures were modeled using template-based modeling, de-novo protein structure prediction, and loop modelin...

Immunostimulation by starch hydrogel-based oral vaccine using formalin-killed cells against edwardsiellosis in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica
Prof. Se Chang Park
abstract
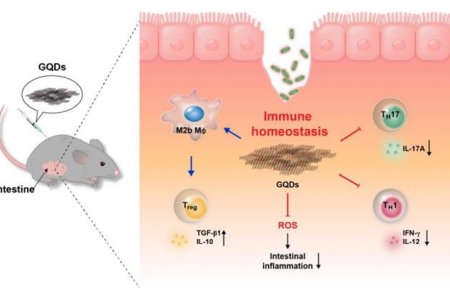
Graphene quantum dots as anti-inflammatory therapy for colitis
Prof. Kyung-Sun Kang
Abstract While graphene and its derivatives have been suggested as a potential nanomedicine in several biomimetic models, their specific roles in immunological disorders still remain elusive. Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) may be suitable for treating intestinal bowel diseases (IBDs) because of their low toxicity in vivo...

The stone-base illusion
Prof. Songjoo Oh
Abstract A popular method used to construct the post structure in traditional Korean buildings is simply placing a stone base on the ground in the natural form and a wooden post on top of the stone base. Interestingly, an illusory visual completion often occurs at the joint where the stone base and the post join. Thus,...
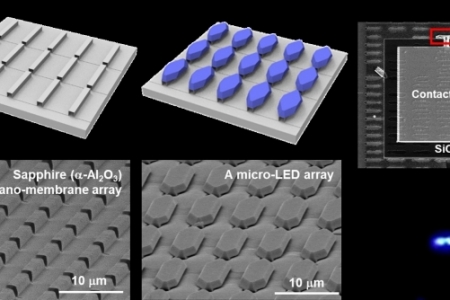
A discrete core-shell-like micro-light-emitting diode array grown on sapphire nano-membranes
Prof. Euijoon Yoon
Abstract A discrete core-shell-like micro-light-emitting diode (micro-LED) array was grown on a 100 nm-thick sapphire nano-membrane array without harmful plasma etching for chip singulation. Due to proper design for the sapphire nano-membrane array, an array of multi-faceted micro-LEDs with size of 4 μm × 16 μm was gro...

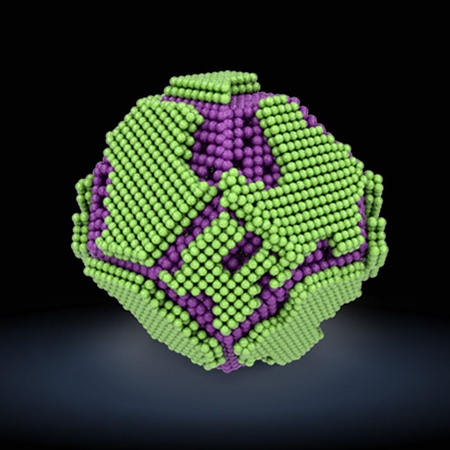
Critical differences in 3D atomic structure of individual ligand-protected nanocrystals in solution
Prof. Jungwon Park
Seeing subtle nanoparticle differences A challenge in the fabrication of nanoparticles is that even for particles of uniform size, there will still be a distribution in the atomic arrangements and surface capping ligands from one particle to the next. Using liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy, Kim et al. recon...

